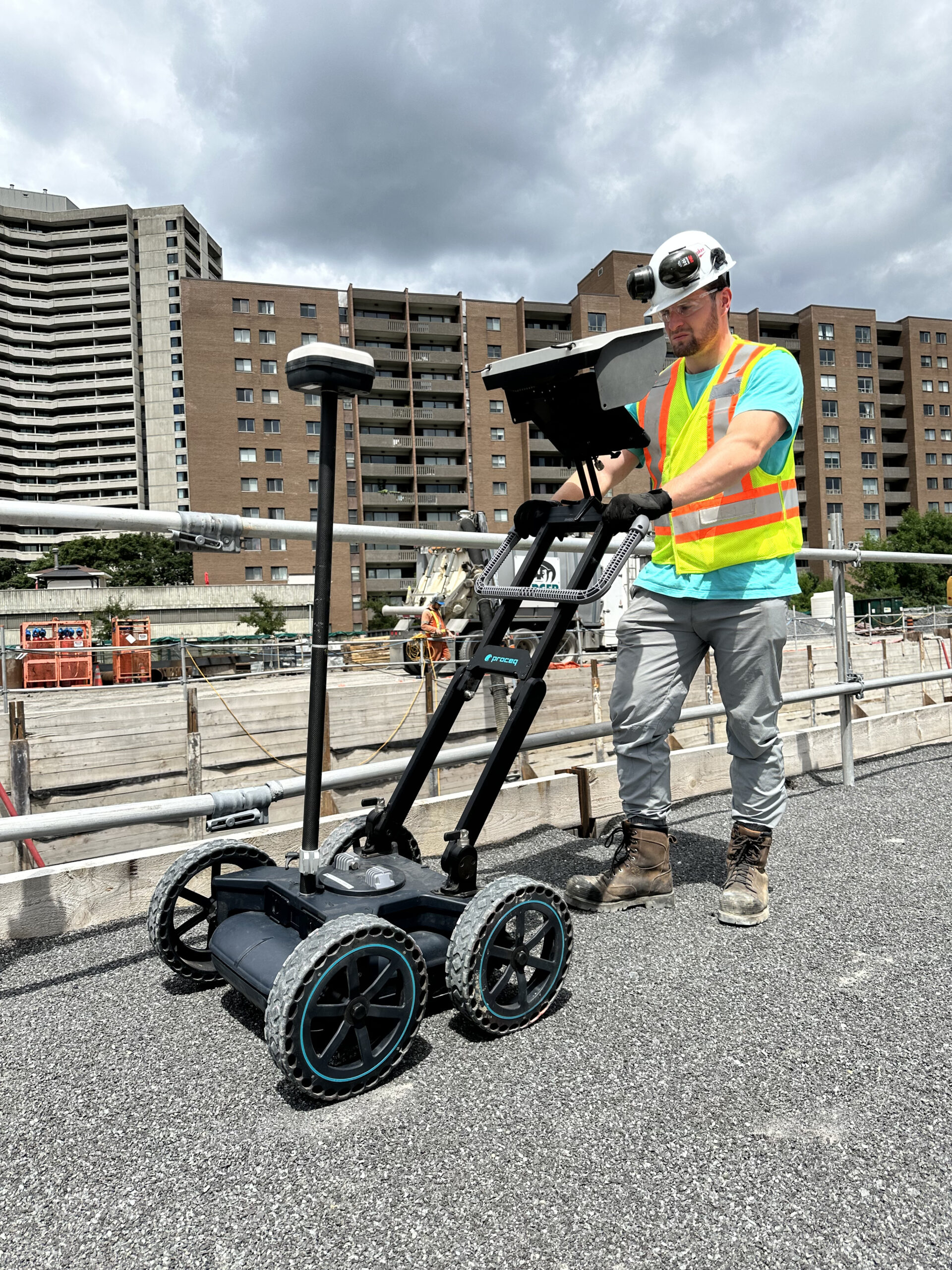
Corrosion Rate Measurement
Corrosion rate measurement is used to quantify the ongoing corrosion activity of steel reinforcement embedded in concrete. Unlike Half Cell Corrosion Mapping that identify whether corrosion may be present, corrosion rate testing provides an estimate of how fast steel loss is occurring, allowing engineers to assess urgency, residual service life, and maintenance priorities.
These methods are commonly applied to bridges, parking structures, marine facilities, industrial slabs, foundations, and other reinforced concrete elements exposed to chlorides, carbonation, or aggressive environments.
Primary Objectives
Corrosion rate measurement in concrete structures aims to:
Quantify the rate of steel corrosion rather than only the likelihood of corrosion
Differentiate between active and passive corrosion zones
Support service life prediction and deterioration modeling
Evaluate the effectiveness of repair, coating, or cathodic protection systems
Prioritize repair timing and scope based on actual deterioration kinetics
Reduce uncertainty in asset management and capital planning decisions
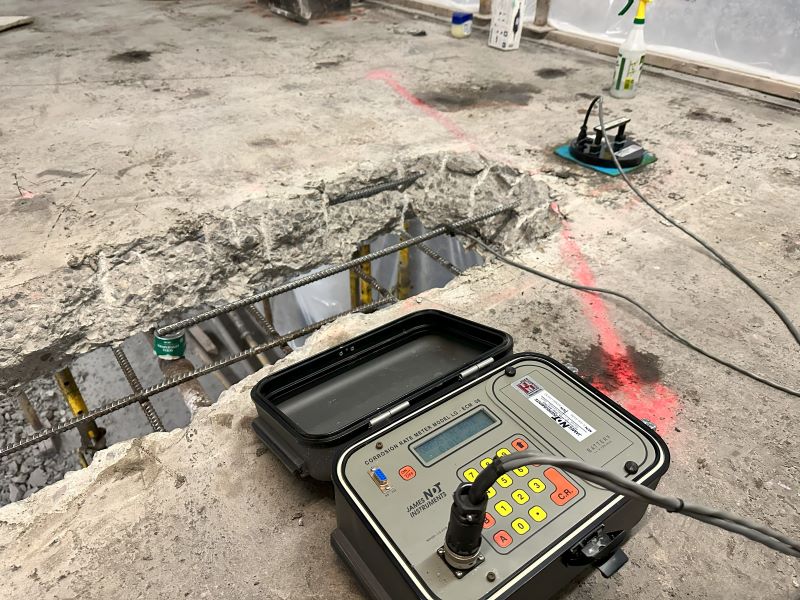

Available Corrosion Rate Measurement Techniques
Linear Polarization Resistance (LPR)
LPR is the most widely used method for direct corrosion rate measurement in reinforced concrete. A small electrical perturbation is applied to the reinforcement, and the resulting polarization response is used to estimate corrosion current density.
Key features:
Provides quantitative corrosion rate values
Suitable for localized testing and detailed investigations
Often combined with half-cell potential mapping
Galvanostatic Pulse Technique
This method applies a short current pulse to the reinforcement and measures the transient voltage response. The results are used to estimate corrosion rate and polarization resistance.
Key features:
Faster testing compared to traditional LPR
Useful for large-area assessments
Well suited for field surveys on bridges and parking structures
What information does Corrosion Rate Measurement Provide?
A corrosion rate assessment typically provides:
Corrosion current density (µA/cm²) or equivalent corrosion rate indicators
Classification of corrosion activity (e.g., low, moderate, high)
Spatial mapping of corrosion severity across structural elements
Correlation with half-cell potential, concrete resistivity, and chloride data (where available)
Engineering interpretation related to expected steel section loss and service life
Recommendations for monitoring, repair, or mitigation strategies
Please contact us for a free quotation and tell us more about your project

