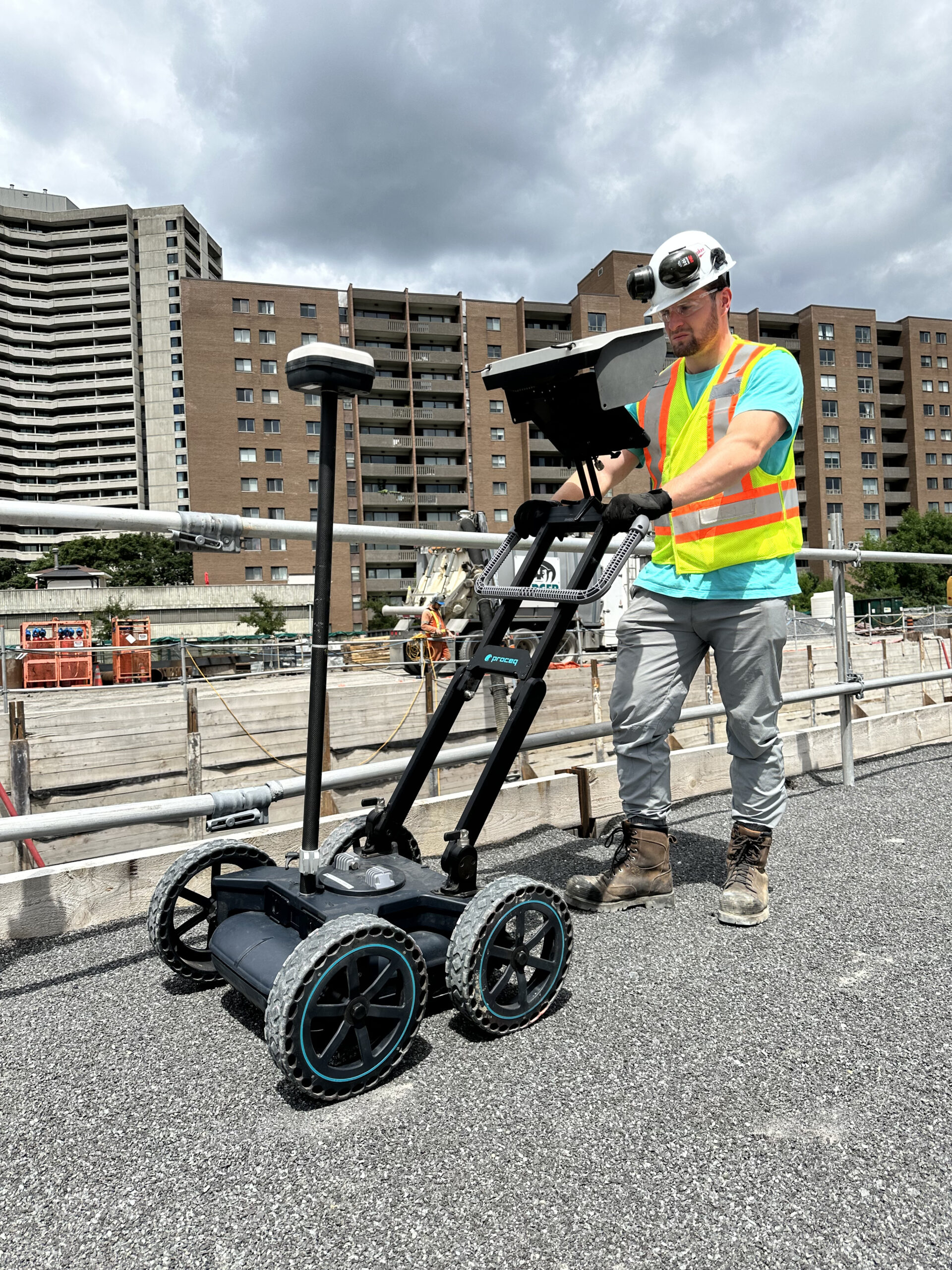
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity – UPV
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) testing is a non-destructive method used to assess the quality, uniformity, and integrity of concrete structures. The test involves measuring the velocity of ultrasonic pulses transmitted through concrete. The speed at which these pulses travel is directly related to the material’s quality; higher velocities generally indicate better concrete quality.
This technique is standardized under ASTM C597, “Standard Test Method for Pulse Velocity through Concrete,” and is widely applied in quality control of new concrete construction, and assessment of existing concrete structures. The UPV test methods can be used to assess the following key performance metrics:
- Concrete uniformity and homogeneity,
- identify potential anomalies, such as cracks.
- Estimate crack depth
The test is performed in various configurations, including direct, semi-direct, and indirect methods, depending on the accessibility of the test surfaces.
Direct UPV
When access to two parallel faces of concrete element is available (beams, columns, or certain walls), the Direct UPV provides the most accurate assessment. In this case, the 2 sensing and receiving transducers will be placed in straight alignment, and the distance between the two transducers is recorded.
UPV = Distance / Time of Flight
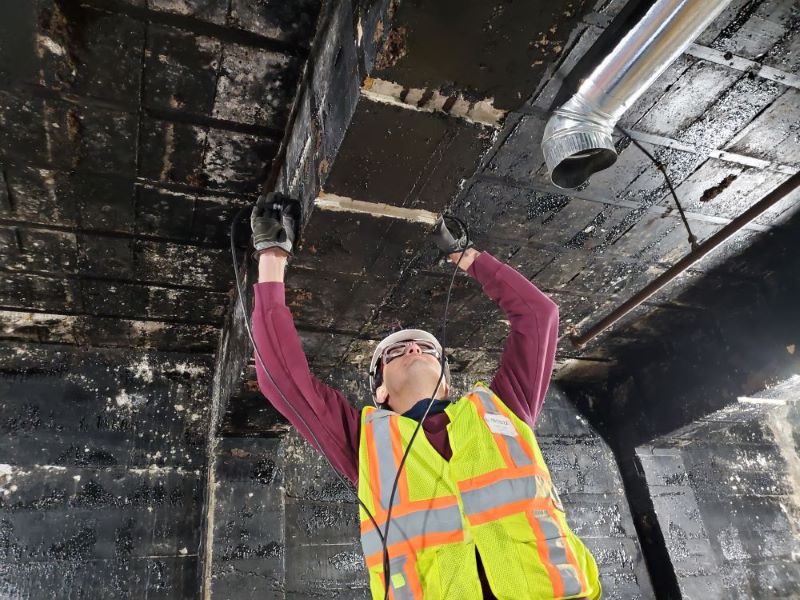

Semi-Direct UPV
When access to the element is feasible through 2 square surfaces, then the UPV probes are placed at equal distances from the edge. This configuration is great for evaluating the extent of cracking on or around the edges of columns, beams or foundations.

In-Direct UPV
The indirect UPV method is particularly useful when access to both sides of the concrete structure is limited, such as perimeter walls, abutment walls, or tunnel linings.
In this method, the transducer and receiver are placed on the same surface, allowing the pulses to travel along the surface rather than through the entire section. This is the least desirable configuration in terms of data accuracy, but also most widely used, since access is generally limited in those elements.
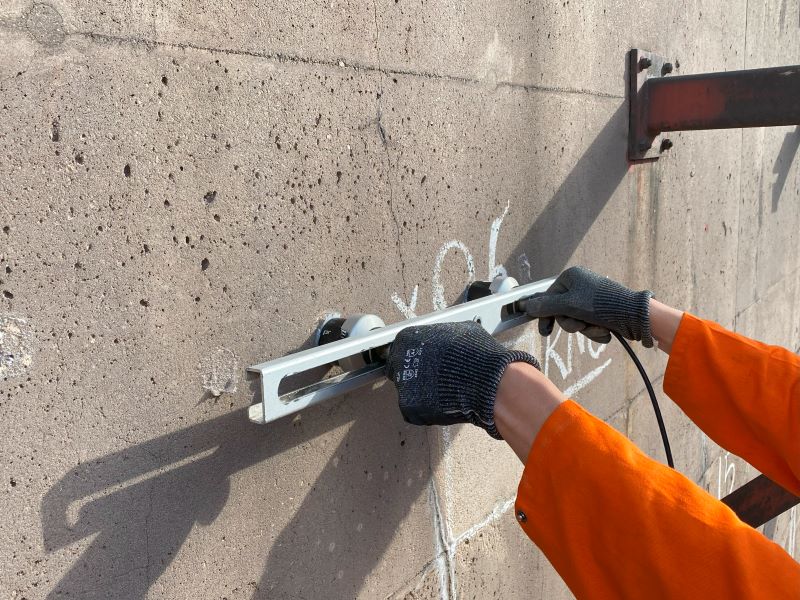

UPV for Crack Depth Estimate
The indirect UPV method can be customized to estimate the depth of cracks in concrete. This make UPV a great tool for evaluating the quality of crack injection before and after repair.
In this method, the two transducers are places on equal distance from the crack line. First, each probe is placed at distance of a from the crack line, and transit time is measured t1.
Later, each probe is placed at distance of 2a from the crack line, and transit is determined, t2.
The Crack Depth is then estimated based on the following mathematical formula:
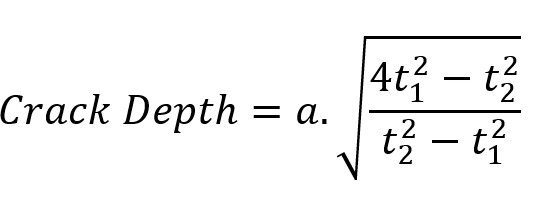

Please contact us for a free quotation and tell us more about your project

